Publication 2007


▼Widely Useful DMAP-Catalyzed Esterification under Auxiliary Base- and Solvent-Free Conditions
Akira Sakakura
Kimio Kawajiri
Takuro Ohkubo
Yuji Kosugi
Kazuaki Ishihara*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14775-14779.
With regard to atom economy and E-factor, catalytic condensation of carboxylic acids with equimolar amounts of alcohols is the most desirable. Although several highly active dehydration catalysts have been reported, more efficient alternatives are still strongly needed because the dehydrative esterification of tertiary alcohols, phenols, acid-sensitive alcohols, amino acids, and hardly soluble alcohols has never proceeded satisfactorily. Here we report new insights into the classical DMAP-catalyzed acylation of alcohols: surprisingly, only a 0.05-2 mol % of DMAP can efficiently promote acylation of alcohols with acid anhydrides under auxiliary base- and solvent-free conditions to give the corresponding esters in high yields. Furthermore, we achieved the recovery and reuse of commercially available polystyrene-supported DMAP without using any solvents. These serendipitous findings provide widely useful and environmentally benign esterification methods, which might be more practical and reliable than catalytic dehydrative condensation methods, in particular, for the less reactive alcohols which hardly condense with carboxylic acid directly.

▼Enantioselective Conjugate Addition of Dialkylzinc to Cyclic Enones Catalyzed by Chiral Binaphthyldiamine-Copper(I) Complexes
Manabu Hatano
Takafumi Asai
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 8590-8594.
▷http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.10.061
The enantioselective conjugate addition of dialkylzinc (R2Zn) to cyclic enones was examined using chiral binaphthyldiamine-copper(I) catalysts. Under the present reaction conditions, chiral C2-symmetric [RZn(II)]2-diamine-Cu(I) complexes were formed from chiral binaphthyldiamine, R2Zn, and copper(I or II) chloride in situ. The reaction of 2-cyclohexenone with Et2Zn proceeded smoothly in the presence of the corresponding chiral copper(I) complex (5 mol %) and achiral 2,6-diphenylaniline (10 mol %), and the desired Et-adduct was obtained with up to 76% ee in 95% yield.
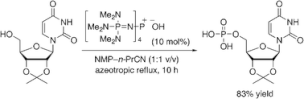
▼Bulky Phosphazenium Cation Catalysis for Dehydrative Condensation of Phosphoric Acid with Alcohols
Akira Sakakura
Mikimoto Katsukawa
Takaomi Hayashi
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Green Chem. 2007, 9, 1166-1169.
Phosphazenium salt provides metal-free direct dehydrative condensation of phosphoric acid with alcohols for the environmentally benign synthesis of phosphoric acid monoesters.

▼Enantioselective Biomimetic Polyene Cyclization of Polyprenoids Long-Sought Enantioselective Reaction Induced by a “Chiral Halonium Ion”
Akira Sakakura
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Chemistry Today 2007, 25(5), 9-12.
Enantioselective biomimetic polyene cyclizations of polyprenoids have been studied for a long time. Very recently, we have developed the first "chiral iodonium ion"- induced enantioselective polyene cyclization of polyprenoids using a nucleophilic promoter. Achiral nucleophilic phosphorus compounds catalytically promote the diastereoselective halocyclization in dichloromethane to give a halogenated cyclic product in excellent yield. Moreover, chiral phosphoramidites stoichiometrically promote the enantioselective halocyclization of simple polyprenoids with N-iodosuccinimide in toluene to give iodinated cyclic products in up to 99 percent ee and 99 percent ds. Some enantioselective polycyclizations have been reported in addition to this halocyclization. One of the advantages of these biomimetic polycyclizations is the simultaneous formation of several carbon-carbon bonds with the relative and absolute stereocontrol. Enantioselective biomimetic domino reactions would be highly useful for the practical synthesis of natural products and related compounds.
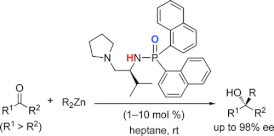
▼Highly Active Chiral Phosphoramide-Zn(II) Complexes as Conjugate Acid-Base Catalysts for Enantioselective Organozinc Addition to Ketone
Manabu Hatano
Takashi Miyamoto
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Org. Lett. 2007, 9(22), 4535-4538.
A highly efficient enantioselective organozinc (R2Zn) addition to ketones catalyzed by chiral phosphoramide-Zn(II) complexes (1-10 mol %) has been developed. These complexes serve as conjugate Lewis acid-Lewis base catalysts. Chiral phosphoramides are derived from an inexpensive natural amino acid (i.e., L-valine). From a variety of nonactivated aromatic and aliphatic ketones, the corresponding optically active tertiary alcohols were obtained in high yields with high enantioselectivities (up to 98% ee) under the mild reaction conditions.
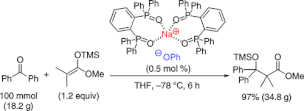
▼Sodium Phenoxide-Phosphine Oxides as Extremely Active Lewis Base Catalysts for the Mukaiyama Aldol Reaction with Ketones
Manabu Hatano
Eri Takagi
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Org. Lett. 2007, 9(22), 4527-4530.
A highly efficient Mukaiyama aldol reaction between ketones and trimethylsilyl enolates catalyzed by sodium phenoxide−phosphine oxides as simple homogeneous Lewis base catalysts (0.5−10 mol %) was developed, which minimized competing retro-aldol reaction. For a variety of aromatic ketones and aldimines, aldol and Mannich-type products with an α-quaternary carbon center were obtained in good to excellent yields. Up to 100 mmol scale of benzophenone and trimethylsilyl enolate with 0.5 mol % of catalyst was established in 97% yield (34.8 g).

▼Rational Design of Minimal Artificial Diels-Alderases Based on the Copper(II) Cation-Aromatic π Attractive Interaction
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Makoto Fushimi
Matsujiro Akakura
Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 1049-1055.
We have designed a minimal artificial metalloenzyme that is prepared in situ from Cu(OTf)2 or Cu(NTf2)2 (1.0 equiv) and L-DOPA-derived monopeptide (1.1 equiv) based on the cation-π attractive interaction between copper(II) and the aromatic arm of the ligand, which is postulated on the basis of X-ray diffraction analysis and theoretical calculations. This catalyst (2-10 mol %) is highly effective for not only the enantioselective Diels-Alder reaction with α,β-unsaturated 1-acyl-3,5-dimethylpyrazoles but also the enantioselective Mukaiyama?Michael reaction with these compounds. Products bearing a 3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl auxiliary may be transformed into a range of carboxylic acid derivatives, such as the corresponding carboxylic acids, esters, amides, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, and β-ketoesters, by known methods. The present results demonstrate that monopeptides are chirally economical and readily tunable ligands compared to bis(oxazoline)s, which have been reported to be notably useful ligands in various enantioselective reactions with bidentate electrophiles.

▼New Boron(III)-Catalyzed Amide and Ester Condensation Reactions
Toshikatsu Maki
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Hisashi Yamamoto*
Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 8645-8657.
▷http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2007.03.157
In 1996, we reported that benzeneboronic acids bearing electron-withdrawing groups at the meta- or para-position are highly effective catalysts for the amide condensation reaction in less-polar solvents. In this paper, we report that N-alkyl-4-boronopyridinium halides are more effective catalysts than the previous ones in more polar solvents. N-Alkyl-4-boronopyridinium halides are effective not only for amide condensation between equimolar mixtures of carboxylic acids and amines but also for the esterification of a-hydroxycarboxylic acids in alcohol solvents. Furthermore, perchlorocatecholborane is more effective than areneboronic acids for the amide condensation of sterically demanding carboxylic acids. In addition, Lewis acid-assisted Bronsted acid (LBA), which is prepared from a 1:2 Mmixture of boric acid and tetrachlorocatechol, is effective for the Ritter reaction from alcohols and nitriles to amides.

▼Catalytic Synthesis of Peptide-Derived Thiazolines and Oxazolines using Bis(quinolinolato)dioxomolybdenum(VI) Complexes
Akira Sakakura
Rei Kondo
Shuhei Umemura
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1641-1646.
Bis(2-ethyl-8-quinolinolato)dioxomolybdenum(VI) (9) (1 mol%) shows remarkable catalytic activity for the dehydrative cyclization of cysteine-containing dipeptides 1 to give the corresponding thiazolines 2 with less than 6% epimerization at the C2-exomethine position. For the dehydrative cyclization of threonine-containing dipeptides 4, 1 mol% of bis(2-phenyl-8-quinolinolato) dioxomolybdenum(VI) (10) gives the corresponding oxazolines 5 with retention of configuration at the 5-position.

▼Direct Ester Condensaton Catalyzed by Bulky Diarylammonium Pentafluorobenzenesulfonates
Akira Sakakura
Shoko Nakagawa
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Nature Protocol 2007, 2(7), 1746-1751.
A protocol for ester condensation between equimolar amounts of carboxylic acids and alcohols catalyzed by bulky diarylammonium pentafluorobenzenesulfonate is described. We also present procedures for the synthesis of N-(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-Nmesitylammonium pentafluorobenzenesulfonate. The present ester condensation proceeds well under mild conditions even without the removal of generated water. The synthesis of N-(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-N-mesitylammonium pentafluorobenzenesulfonate will take 5 days. The ester condensation reactions will take 6 h to 3 days.
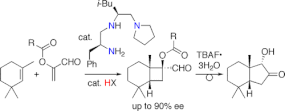
▼Enantioselective [2 + 2] Cycloaddition of Unactivated Alkenes with -Acyloxyacroleins Catalyzed by Chiral Organoammonium Salts
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Kazuhiko Nakano
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8930-8931.
We report the first example of an organocatalytic enantioselective [2 + 2] cycloaddition reaction of unactivated alkenes with -acyloxyacroleins to give optically active 1-acyloxycyclobutanecarbaldehydes and subsequent ring expansion to give optically active 2-hydroxycyclopentanone derivatives. Organoammonium salt, H-L-Phe-L-Leu-N(CH2CH2)2-reduced triamine2.6HNTf2, is a highly effective chiral catalyst for the above enantioselective [2 + 2] cycloaddition. Thus, we have developed a novel and useful formal enantioselective [2 + 3] cycloaddition through two steps.

▼Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Alcohols Catalyzed by Minimal Artificial Acylases Derived from L-Histidine
Yuji Kosugi
Matsujiro Akakura
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 6191-6203.
▷http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2007.02.020
The artificial acylases, tert-butyldiphenylsilyl ether and tris(trimethylsilyl)silyl ether of N(p)-methyl-N(a)-(2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonyl)-L-histidinol, are simple and small molecules, which contain only one chiral carbon center that originates from natural L-histidine. Asymmetric acylation of racemic secondary alcohols with isobutyric anhydride induced by these artificial acylases gave optically active isobutyrates and optically active alcohols with an S(kfast-reacting enantiomer/kslow-reacting enantiomer) value of up to 132. One hydrogen bonding interaction between a sulfonamidyl group of the catalysts and a substrate should be essential for inducing the high level of kinetic resolutio through catalytic asymmetric acylation. Furthermore, a reusable polystyrene-bound artificial acylase was developed to examine its practicality.

▼Dehydrative Cyclization Catalyzed by the Combination of Molybdenum(VI) Oxides and Benzoic Acids: First Synthesis of the Antitumour Substance BE-70016
Akira Sakakura
Shuhei Umemura
Rei Kondo
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349(4-5), 551-555.
The dehydrative cyclization of N-(o-hydroxybenzoyl)threonine derivative 1a is efficiently promoted by the combined use of molybdenum(VI) oxides and benzoic acids bearing electron-withdrawing substituents. In the presence of ammonium molybdate [(NH4)2MoO4, 10 mol %] and pentafluorobenzoic acid (C6F5CO2H; 10 mol %), dehydrative cyclization of 1a was conducted in toluene under azeotropic reflux conditions to give 2-(o-hydroxyphenyl)oxazoline 2a in 76 % yield. Furthermore, the first total synthesis of the antitumour substance BE-70016 was achieved using the catalytic dehydrative cyclization of 1a as a key reaction.

▼Unusual Rate Acceleration in Bronsted Acid Catalyzed Dehydration Reactions: Local Hydrophobic Environment in Aggregated N-(2,6-diphenylphenyl)-N-mesitylammonium Pentafluorobenzenesulfonates
Akira Sakakura
Hitoshi Watanabe
Shoko Nakagawa
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Chem. Asian J. 2007, 2(4), 477-483.
Bulky diarylammonium pentafluorobenzenesulfonates effectively promote dehydration reactions, such as condensation reactions to give esters and the dehydrative cyclization of 1,3,5-triketones. In particular, N-(2,6-diphenylphenyl)-N-mesitylammonium pentafluorobenzenesulfonate shows much higher catalytic activity than C6F5SO3H under reaction conditions without the removal of generated water, even though the former is a weaker acid. Its crystallization gives an aggregated cyclic ion pair, which is composed of two diarylammonium cations, four pentafluorobenzenesulfonate anions, and two oxonium cations. This ion pair is strongly stabilized by four intermolecular and two intramolecular p-p attractive interactions and 10 hydrogen bonds. The extremely high catalytic activity of N-(2,6-diphenylphenyl)-N-mesitylammonium pentafluorobenzenesulfonate in the dehydration reactions may be ascribed to the local hydrophobic environment of the tightly aggregated ammonium salts.
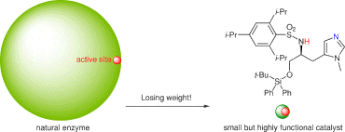
▼Design of Highly Functional Small-Molecule Catalysts and Related Reactions Based on Acid-Base Combination Chemistry
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Akira Sakakura
Manabu Hatano
Synlett 2007, 686-703.
▷DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-970776
The design of small but highly functional artificial catalysts is very important for practical organic synthesis. We have -succeeded in the rational design of small and simple catalysts and related reactions based on acid-base combination chemistry. Acid-base combined catalysts can be classified into three types: (i) acid-base combined salt catalysts, (ii) conjugate acid-base catalysts, and (iii) nonconjugate acid-base catalysts. We have systematically developed acid-base combined salt catalysts such as ammonium salts, ate complexes, ion pairs and cation-pi complexes, acid-base conjugate catalysts such as metal oxides (monoconjugation) and zinc(II)-3,3′-diphosphinol-BINOLates (triconjugation), and acid-base nonconjugate catalysts like l-histidine-derived sulfonamides.

▼Enantioselective Halocyclization of Polyprenoids Induced by Nucleophilic Phosphoramidites
Akira Sakakura
Atsushi Ukai
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Nature 2007, 445, 900-903.
▷DOI: 10.1038/nature05553
Polycyclic bio-active natural products that contain halogen atoms have been isolated from a number of different marine organisms1. The biosynthesis of these natural products appears to be initiated by an electrophilic halogenation reaction at a carbon.carbon double bond2.4 via a mechanism that is similar to a proton-induced olefin polycyclization5.8. Enzymes such as haloperoxidases generate an electrophilic halonium ion (or its equivalent), which reacts with the terminal carbon.carbon double bond of the polyprenoid, enantioselectively inducing a cyclization reaction that produces a halogenated polycyclic terpenoid. Use of an enantioselective halocyclization reaction is one possible way to chemically synthesize these halogenated cyclic terpenoids; although several brominated cyclic terpenoids have been synthesized via a diastereoselective halocyclization reaction that uses stoichiometric quantities of a brominating reagent9.12, the enantioselective halocyclization of isoprenoids induced by a chiral promoter has not yet been reported. Here we report the enantioselective halocyclization of simple polyprenoids using a nucleophilic promoter. Achiral nucleophilic phosphorus compounds are able to promote the diastereoselective halocyclization reaction to give a halogenated cyclic product in excellent yields. Moreover, chiral phosphoramidites promote the enantioselective halocyclization of simple polyprenoids with N-iodosuccinimide to give iodinated cyclic products in up to 99% enantiomeric excess and diastereomeric excess. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first successful example of the enantioselective halopolycyclization of polyprenoids.

▼N-Monoacylureas, and Alpha-Substituted Ketoximes to Nitrile Compounds
Yoshiro Furuya
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Hisashi Yamamoto*
Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 80(2), 400-406.
▷http://dx.doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.80.400
The dehydration reaction of primary amides is one of the most fundamental methods for the synthesis of nitriles, and the development of environmentally benign catalytic reaction processes is needed. We surveyed a variety of metal catalysts and found that perrhenic acid was extremely effective for the dehydration of not only primary amides but also aldoximes. Typically, 1 mol % of perrhenic acid gave the corresponding nitriles from amides or aldoximes under azeotropic reflux conditions with the removal of water in toluene or mesitylene. In addition, perrhenic acid is an extremely efficient catalyst for the Beckmann fragmentation of α-substituted ketoximes to functionalized nitriles. This new catalytic system can be applied to the gram-scale synthesis of nitriles without further modifications.

▼The Oxorhenium(VII)-Catalyzed Direct Condensation of Phosphoric Acid with an Alcohol
Akira Sakakura
Mikimoto Katsukawa
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46(9), 1423-1426.
▷DOI: 10.1002/anie.200604333
Oxorhenium-(VII) complexes catalyze the direct condensation of phosphoric acid with an alcohol to selectively give the corresponding a 2-100-mmol scale method should be useful industrially important synthesis acid monoesters.

▼Recent Progress in Selective Additions to Organometal Reagents to Carbonyl Compounds
Manabu Hatano
Takashi Miyamoto
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Curr. Org. Chem. 2007, 11(2), 127-157.
▷DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/138527207779316453
Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions are simple and direct methods for synthesizing the various skeletons and the diverse structures of organic compounds. Even 100 years after the discovery of
the Grignard reaction, organomagnesium, organolithium, and organoaluminum remain popular for carbon-carbon bond formation reactions in modern organic chemistry. Moreover, asymmetric alkyl- or
aryl-additions to carbonyl compounds with organometal reagents is attractive due to the enantioselective synthesis of chiral secondary alcohols, which sharply contrasts the enantioselective
reduction of carbonyl compounds. Herein, we review recent progress in the selective addition to carbonyl compounds with organometal reagents, particularly Li, Mg, and Zn from both a classic
viewpoint using metal ate complexes and from a catalytic enantioselective viewpoint using new chiral ligands.







